HIV/AIDS in Africa
Africa is the continent most affected by the AIDS epidemic, with more than 65% of cases.
Epidemiology:
34 to 46 million people worldwide are infected with AIDS. In 2003 alone, more than 3 million people died.
That same year, Africa whose population is only 11% of the world population,
was home to 2/3 of all patients with HIV in the world. Today,
one African out of 12 is carrying the virus and/or sick.
The impact of the disease is not only measured by the number of deaths.
The social consequences are major. AIDS destroys the efforts made to enable
the empowerment of women, destroys the slow progress in terms of education,
impact people's health care (in South Africa today, 80% of patients
hospitalized in public hospitals are HIV positive. Malaria is going down but tuberculosis
and diseases related to malnutrition are progressing rapidly). Population growth in Africa has stopped.
Perinatal mortality is up dramatically. Life expectancy has dropped to 49 years
in southern African countries while it is 78 years in Europe and North America.
Throughout the world, people aged between 20 and 40 years old are most affected.
This means that the forces, economic drivers of African countries,
are missing. The economic impact is considerable.
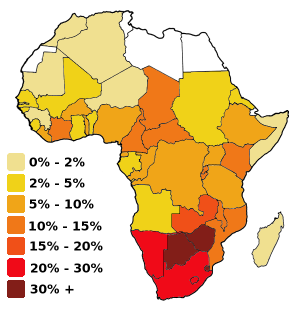 Map of Africa coloured according to the percentage of the Adult (ages 15-49) population with HIV/AIDS.
Map of Africa coloured according to the percentage of the Adult (ages 15-49) population with HIV/AIDS.
 Life expectancy changes in several African countries
Life expectancy changes in several African countries

